TRADE CONDITION (INCOTERMS)
In terms of INCOTERMS (International Commercial Terms), the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) establishes routine terms and conditions, especially the costs and risks between parties concerning import and export transactions.
It began to establish international rules on the interpretation of standardized trading conditions in 1936, in order to prevent errors in business conditions arising from differences in the business practices of importing and exporting from country to country and for preventing disputes and litigation.
INCOTERMS 2020 ALL 11 SPECIES
EXW (Ex Works) …Factory migration
The seller’s delivery obligation is the same as CPT, but the buyer is responsible for transportation costs and freight forwarding insurance premiums to the designated destination. CIP conditions require that the buyer obtain an insurance with minimum coverage.

FCA (Free Carrier) …passenger
The seller’s delivery obligation is completed when the agreed goods are handed over to the carrier designated by the buyer at the designated location. The export clearance procedure is done by the seller. If the place of delivery is within the vendor’s facility, the seller is responsible for loading. In the case where the delivery place is other than this, the seller is not responsible for unloading. If the buyer nominates a person or a freight forwarder instead of the carrier to receive the goods, the delivery will be completed when the goods are in the custody of the person.

CPT (Carriage Paid to) …Transportation cost included
The seller pays the freight for the carriage of the goods to the named destination. After the goods are delivered to the carrier, the buyer will bear all risks and any additional costs. Export customs clearance procedures are carried out by the seller.

CIP…Shipping cost insurance premium
The seller’s delivery obligation is the same as CPT, but the buyer is responsible for transportation costs and freight forwarding insurance premiums to the designated destination. CIP conditions require that the buyer obtain an insurance with minimum coverage.

DPU… Delivery Place Unloaded
The seller fulfills the obligation to deliver (risk transfer) when it is left to the buyer’s disposition after the goods are unloaded from the transportation means at the designated terminal in the destination port or the destination. The export clearance procedure is done by the seller.

DAP (Delivered at Port) … Destination place carry-in delivery
The seller fulfills the duty of delivery (risk transfer) when the goods are left to the buyer’s disposition on the port of arrival and is ready for unloading. Export clearance procedures are carried out by the seller, but there is no obligation for import clearance. However, DDP should be selected if the seller wish to include import clearance procedures.

DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)…Tariff carry-in handover
Delivered duty paid means that the seller fulfils his obligation to deliver when the goods have arrived at the designated destination. The seller has to bear the risks and costs, including duties, taxes and other charges of delivering the goods, and cleared for importation. DDP represents the maximum obligation for the seller

FAS (Free Alongside Ship) …Ship side transfers
The seller fulfils his obligation to deliver when the goods have been placed alongside the vessel on the quay or in lighters at the named port of shipment. This means that the buyer has to bear all costs & risks of loss of / damage to the goods from that moment. The FAS term requires the buyer to clear the goods for export..

FOB (Free On Board)
The seller fulfils his obligation to deliver when the goods have passed over the ship’s rail at the named port of shipment. This means that the buyer has to bear all costs & risks of loss of or damage to the goods from that point. The seller is also required to clear the goods for export.
CFR (Cost and Freight) …Fare included
The seller must pay the costs & freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination. The buyer bears the risk of loss of / damage to the goods, as well as any additional costs after the goods have been delivered on board the vessel. Meanwhile, the seller are required to clear the goods for export.

CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) Fare insurance included
The seller has the same obligations as under CFR but with the addition that he has to procure marine insurance against the buyer’s risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage. The seller contracts for insurance & pays the insurance premium. However, under the CIF term the seller is only required to obtain insurance on minimum coverage and to clear the goods for export.

CONTAINER

Internationally standardized containers are required to smoothly operate an integrated transportation system for containers, and for that purpose, the dimensions, strength, external form, etc. are standardized by the International Standardization Organization (ISO).
Dry Container
It is the most popular and is used for various general cargo transportation.
Special container
(a) Refrigerated Container
It is aimed to transport frozen and refrigerated cargo (fresh food such as fruits, vegetables, meat, fish and shellfish, as well as chemical products such as film). Generally it has a built-in freezing unit and can keep the prescribed temperature.
(b) Open Top Container
Bulky objects and heavy items are transported and loaded from the top by opening the roof portion.
(c) Flat Rack Container
It has a structure that can handle loading from the left and right side, without holding the roof part, the side faces, and the door face. Designed for long articles, heavy goods, or large cargoes that cannot be packed in containers.
Container type
There are two types of container materials: Aluminum Containers and Steel Containers. The ISO standardized dimensions, strength, external form, shape, etc. of a container is classified for its intended purpose and structure as follows:
(a) Flat Bed Container
Similar to a flat rack container, it is intended for large cargoes that cannot normally be packed in containers and has no upper structure at all.
(b) Tank Container
Designed for liquid cargo such as malt (sake), soy sauce, foodstuffs, liquid chemicals and the like, with tanks stored in the steel frame.
In addition to the above, new type of container development is expected to increase further in the future, in order to respond to changes in international logistics products and the requests to streamline distribution system efficiency.
Additionally, the container will always have a jersey number so that the owner, type and size of the container can be known at a glance. This numbering system is internationally standardized by ISO. In addition, marked containers signifies international approval of special convenience.
CONTAINER SIZE
Dry container size
In the most standard size, there are the 20 feet container (8’x 8′ 6′ x 20′) and the 40′ container (8’x 8′ 6 ‘x 40′). As of June 1, 1985, domestic regulation has permitted the domestic passage of containers with a height of 8’× 9′ 6’× 40’.
| External Dim | Length | 6,058mm | 12,192mm | 12,192mm |
| (19’10” 1/2) | (40’0”) | (40’0”) | ||
| Width | 2,438mm | 2,438mm | 2,438mm | |
| (8’0”) | (8’0”) | (8’0”) | ||
| Height | 2,591mm | 2,591mm | 2,896mm | |
| (8’6”) | (8’6”) | (9’6”) | ||
| Internal Dim | Length | 5,899mm | 12,033mm | 12,033mm |
| (19’4” 1/4) | (39’5” 3/4) | (39’5” 3/4) | ||
| Width | (2,352mm) | (2,352mm) | (2,352mm) | |
| (7’8” 5/8) | (7’8” 9/16) | (7’8” 5/8) | ||
| Height | 2,386mm | 2,386mm | 2,691mm | |
| (7’9” 15/16) | (7’9” 15/16) | (8’9” 15/16) | ||
| Internal Capacity | 33.1m3 | 67.5m3 | 76.2m3 | |
| Door Open | Wide | 2,340mm | 2,340mm | 2,340mm |
| (7’8” 1/8) | (7’8” 1/8) | (7’8” 1/8) | ||
| Height | 2,272mm | 2,272mm | 2,577mm | |
| (7’5” 7/16) | (7’5” 7/16) | (8’5” 1/2) | ||
| Tare Weight | 2,220kg | 3,740kg | 3,920kg | |
| (4,890lbs) | (8,250lbs) | (8,640lbs) | ||
| Payload | 21,780kg | 26,740kg | 26,560kg | |
| (48,020lbs) | (58,950lbs) | (58,560lbs) | ||
| Gross Weight | 24,000kg | 30,480kg | 30,470kg | |
| (52,910lbs) | (67,200lbs) | (67,200lbs) |
Size of refrigerated container
The refrigerator is built in the refrigerated container, while the heat insulator is installed inside the container, while the rail is attached to the floor part, causing the content amount and the maximum load weight to be slightly smaller compared to the dry container. As for the standard sizes, 20 ‘and 40’, are the same as dry container.
| External Dim | Length | 6,058mm | 12,192mm |
| (19’10” 1/2) | (40’0”) | ||
| Width | 2,438mm | 2,438mm | |
| (8’0”) | (8’0”) | ||
| Height | 2,591mm | 2,896mm | |
| Internal Dim | Length | 5,486mm | 11,669mm |
| Width | 2,270mm | 2,286mm | |
| (7’5” 3/8) | (7’6”) | ||
| Height | 2,263mm | 2,508mm | |
| (7’5” 3/32) | (8’2” 3/4) | ||
| Internal Capacity | 27.8m3 | 66.9m3 | |
| (982cft) | (2,363cft) | ||
| Door Open | Wide | 2,270mm | 2,286mm |
| (7’5” 3/8) | (7’6”) | ||
| Height | 2,198mm | 2,437mm | |
| (7’2” 1/2) | (7’11” 15/16) | ||
| Tare Weight | 2,750kg | 4,600kg | |
| (6,060lbs) | (10,140lbs) | ||
| Payload | 21,250kg | 25,880kg | |
| (46,850lbs) | (57,060lbs) | ||
| Gross Weight | 24,000kg | 30,480kg | |
| (52,910lbs) | (67,200lbs) |
TRUCKING
Box Type 1
Inside dimension 242(length)×162(width)×134(height)cm
Outer dimension 253(length)×170(width)×162(height)cm
Door size 147(width)×122(height)cm
Box Type 2
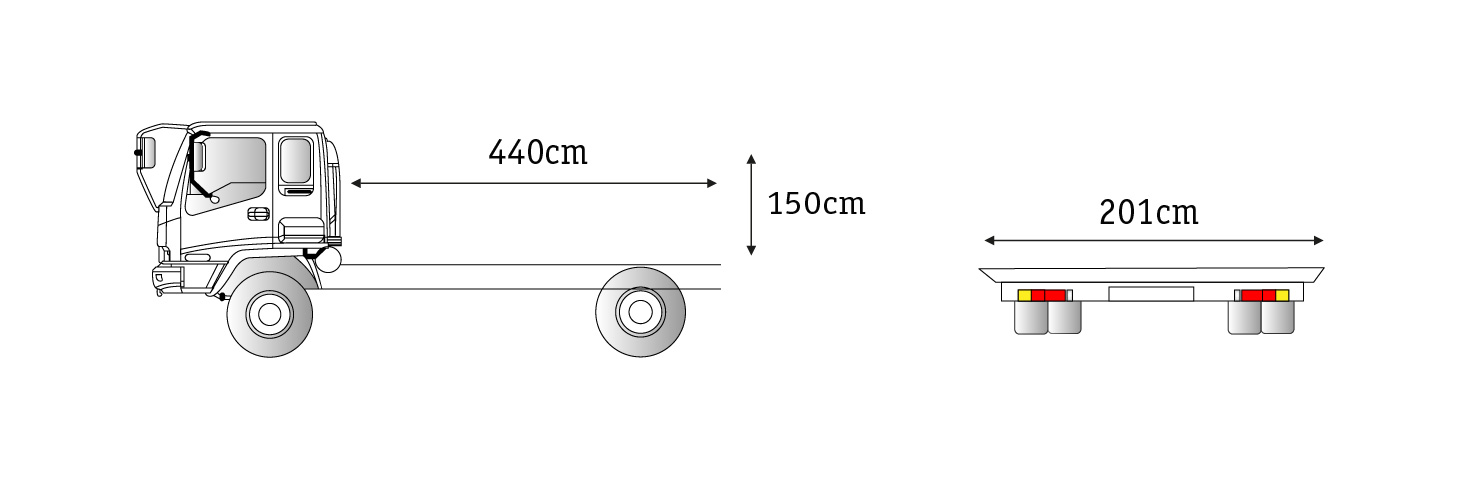
Inside dimension 435(length)×197(width)×198(height)cm
Outer dimension 449(length)×210(width)×201(height)cm
Door size 190(width)×182(height)cm
Box Type 3
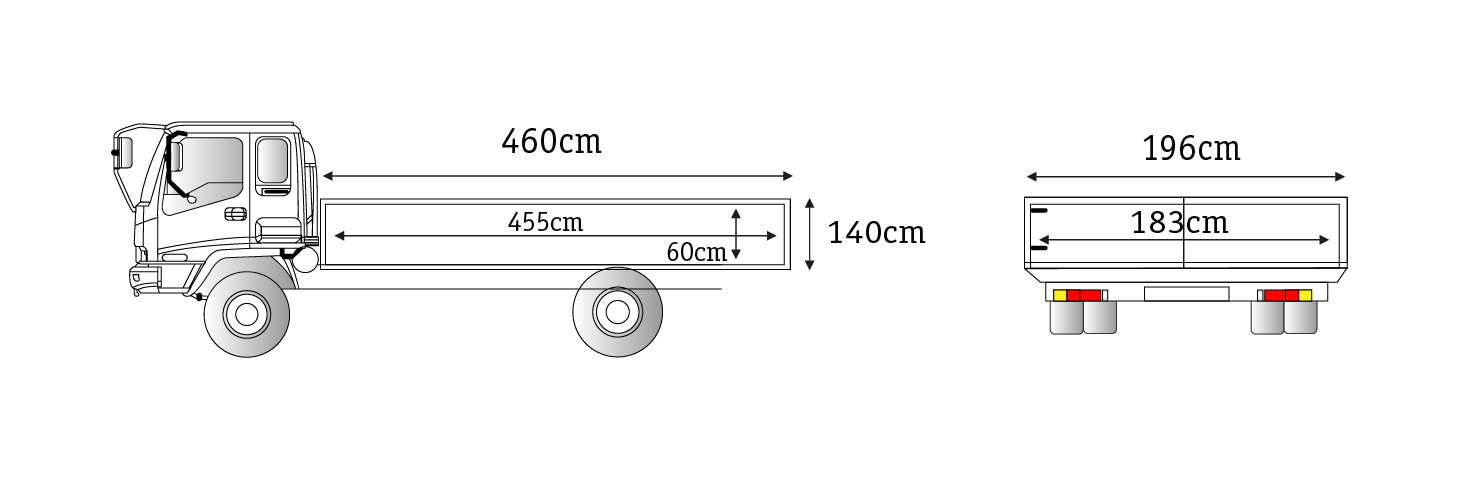
Inside dimension 455(length)×183(width)×60(height)cm
Outer dimension 460(length)×196(width)×140(height)cm

PT Cakra Mitra International
PT Cakra Gemilang Prakasa
Jl. Mampang Prapatan Raya No.67, Tegal Parang,
Mampang Prapatan, Jakarta - 12790 Indonesia
TEL: (+62) 21-79192947
Bekasi Warehouse
Kp. Awirarangan RT.001/005, Desa Tamansari, Setu,
Bekasi - 17320, Indonesia
Cakung Warehouse
Green Sedayu Biz Park Cakung GS 16 No. 21,
Cakung Timur, Cakung,
Jakarta Timur-13910, Indonesia
PT Logicom Cakra Indonesia
Jl. Anggrek VII, KITIC, Nagasari, Serang Baru,
Bekasi-17330, Indonesia
Cakra International Co.,Ltd.
Matsushita Building 2nd Floor.
2-12-13, Shinkawa, Chuo-Ku.
Tokyo, Japan, 104-0033
TEL: (+81) 3-58298718
Service
© 2026 PT Cakra Mitra International | All Rights Reserved